Meeting Global Standards, Exceeding Expectations
- About Us
- Applications
- quality assurance
- Standards
ASTM Standard
The (ASTM) American Society for Testing and Materials has developed different standard & specification for Bolt fasteners for variety of uses. ASTM’s fastener standards are instrumental in specifying, testing, and evaluating the material, dimensional, mechanical, and metallurgical properties of the various forms of hardware fasteners. These fasteners are used to mechanically join or affix other hardware objects together, and come in many forms which include rivets, nuts, bolts, studs, screws, washers, eyebolts, nails, and threaded fasteners. These fastener standards allow hardware product manufacturers, as well as the end-users of such products, to examine and assess fasteners to ensure their strength and quality towards safe utilisation.

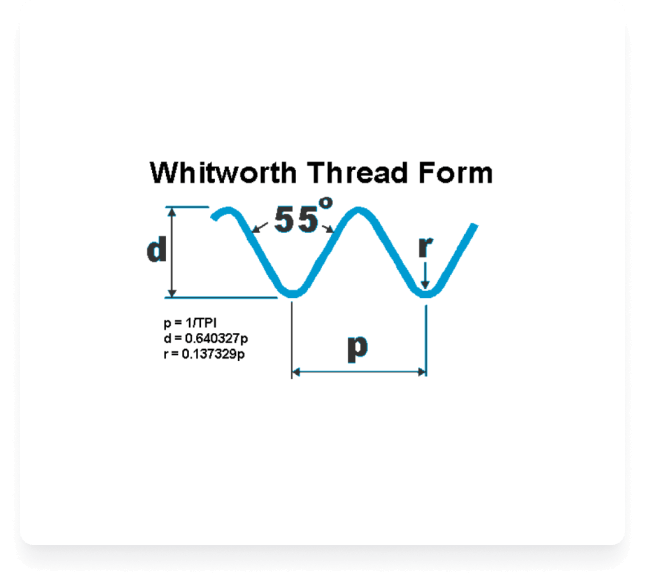
British Standard Whitworth
Sir Joseph Whitworth proposed this thread in 1841. This was the first standardised thread form. The form of the thread is shown in the diagram. The principal features of the British Standard Whitworth (BSW) thread form are that the angle between the thread flanks is 55 degrees and the thread has radii at both the roots and the crests of the thread.
The relevant standard for this thread form is the British Standard BS 84 – 2007. The thread form is now redundant and has been replaced by Unified and Metric threads but there are many applications in which it is still used. The British Standard Fine (BSF) thread has the same profile as the BSW thread form but was used when a finer pitch was required for a given diameter.
ISO Standard
The ISO metric screw threads are the most commonly used type of general-purpose screw thread worldwide. They were one of the first international standards agreed when the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) was set up in 1947. The “M” designation for metric screws indicates the nominal outer diameter of the screw thread, in millimetres (e.g., an M6 screw has a nominal outer diameter of 6 millimetres). Our team identifies, sources, and supplies the necessary materials that align with Saudi Arabia’s stringent industrial standards, including Aramco and SABIC compliance requirements.


SAE Standard
The SAE has established a sequence of grades from 0 to 8 for steel bolts, on the basis of the metal from which the bolt is made and the manner of manufacture. Available grades run from 2 to 8, with 8 the strongest. Higher grade numbers almost always mean increased strength (an exception is that some grade 6 bolts are stronger than grade 7). The heads of steel bolts are marked to identify their grade. Allen bolts usually exceed strength capacity of hexagonal bolts.
JIS Standard
Japanese Industrial Standards(JIS) specifies the standards used for industrial activities in Japan. The standardization process is coordinated by the Japanese Industrial Standards Committee (JISC) and published through the Japanese Standards Association (JSA). Japanese Industrial Standards Committee is composed of many nationwide committees and plays vital role in standardizing activities in Japan. JIS bolts are a type of metric bolt as opposed to the U.S. standard.
JIS bolts reflect the philosophies of design and manufacture many Japanese industries have become world renowned for. With things getting smaller, so too do fastening standards need to facilitate smaller parts.
The difference between JIS bolts and other metric bolts is the head size. Lighter, more compact designs have necessitated the use of lighter, more compact fastening accessories. Basically, ISO (International Standardization Organization and ANSI (American National Standard) bolt standards use bigger heads than JIS types.